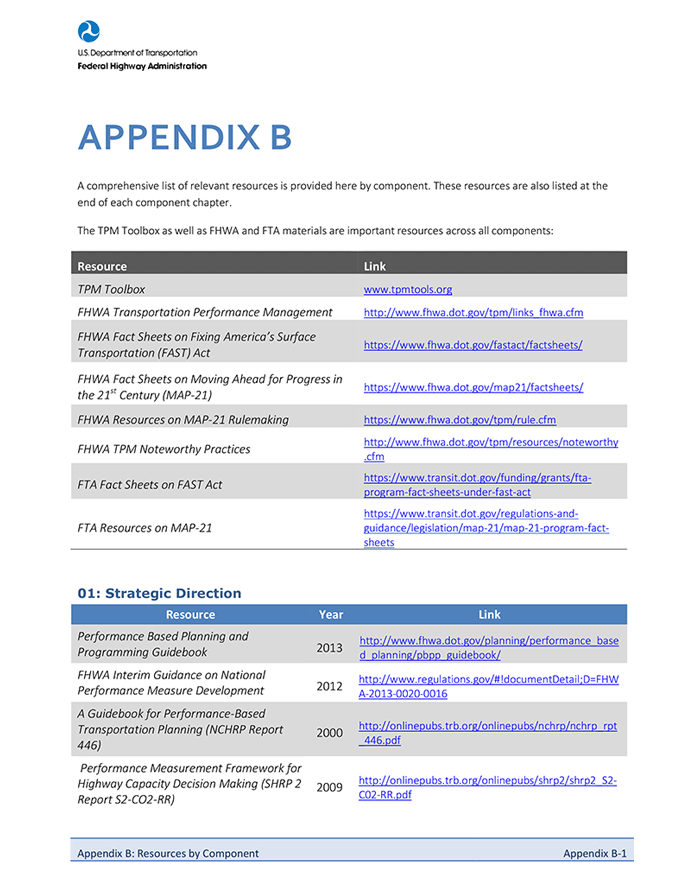
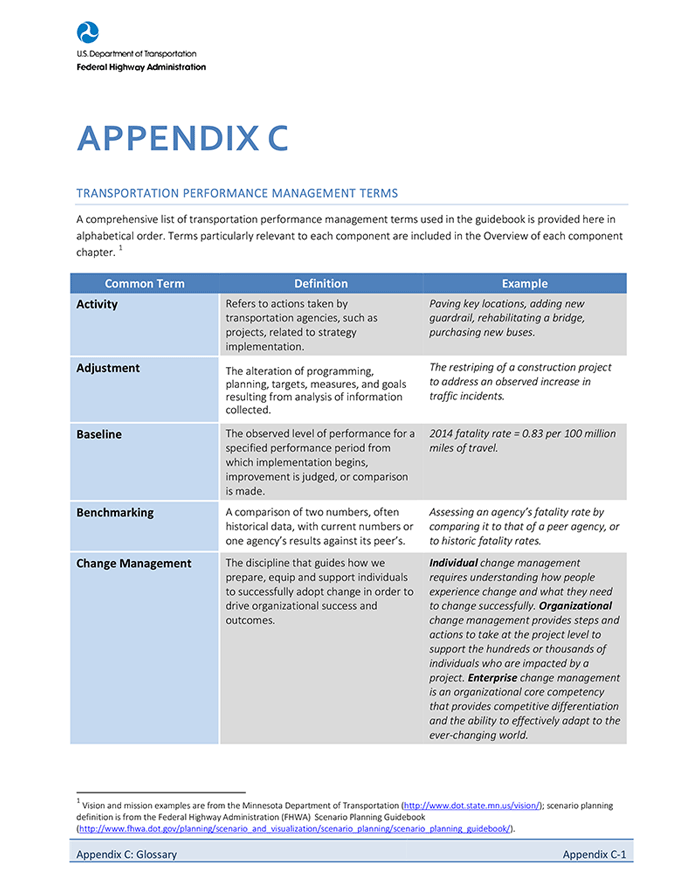
TPM Guidebook
Building upon over a decade of transportation performance management research and agency practices, this guidebook introduces a comprehensive TPM Framework. Each numbered and lettered component below is discussed in a dedicated chapter within the guidebook. Summary factsheets are also available for each component. Each Guidebook chapter is also available to download as a PDF file.
Introduction. TPM Framework
Component 1. Strategic Direction
A Strategic Direction establishes an agency’s direction through well-defined goals and objectives and enables assessment of the agency’s progress towards meeting goals by defining a set of aligned performance measures. The Strategic Direction is the foundation upon which all performance management rests and should be included in an agency’s business plan.
Component 2. Target Setting
Target setting is the use of baseline data, information on possible strategies, resource constraints, and forecasting tools to collaboratively establish a quantifiable level of performance the agency wants to achieve within a specific time frame. Targets make the link between investment decisions and performance expectations transparent across all stakeholders.
Component 3. Performance-Based Planning
Performance-Based Planning is the use of agency goals and objectives and performance trends to drive development of strategies and priorities in the long-range transportation plan and other performance-based plans and processes. The resulting planning documents become the blueprint for how an agency intends to achieve its desired performance outcomes.
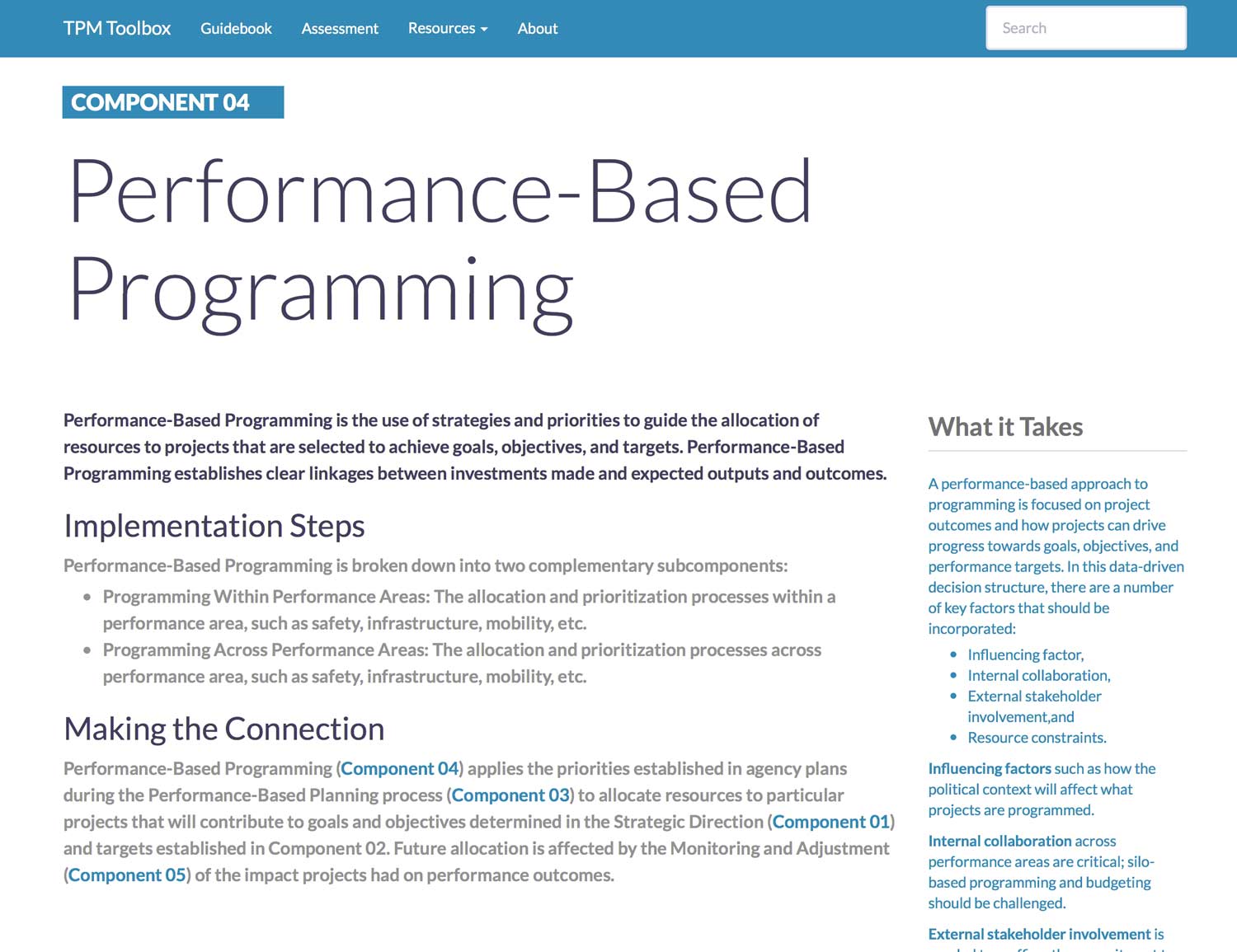
Component 4. Performance-Based Programming
Performance-Based Programming is the use of strategies and priorities to guide the allocation of resources to projects that are selected to achieve goals, objectives, and targets. Performance-Based Programming establishes clear linkages between investments made and expected outputs and outcomes.
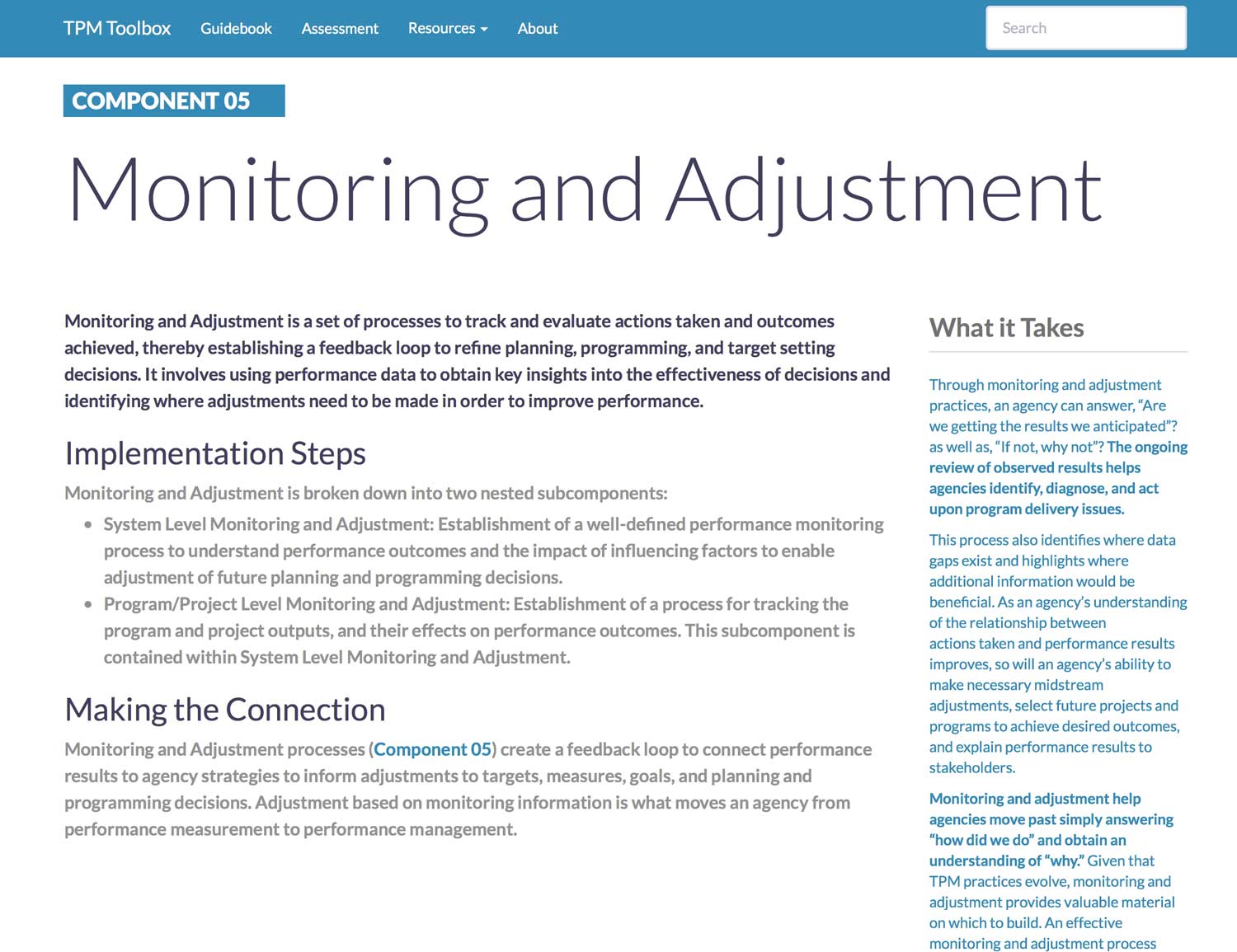
Component 5. Monitoring and Adjustment
Monitoring and Adjustment is a set of processes to track and evaluate actions taken and outcomes achieved, thereby establishing a feedback loop to refine planning, programming, and target setting decisions. It involves using performance data to obtain key insights into the effectiveness of decisions and identifying where adjustments need to be made in order to improve performance.
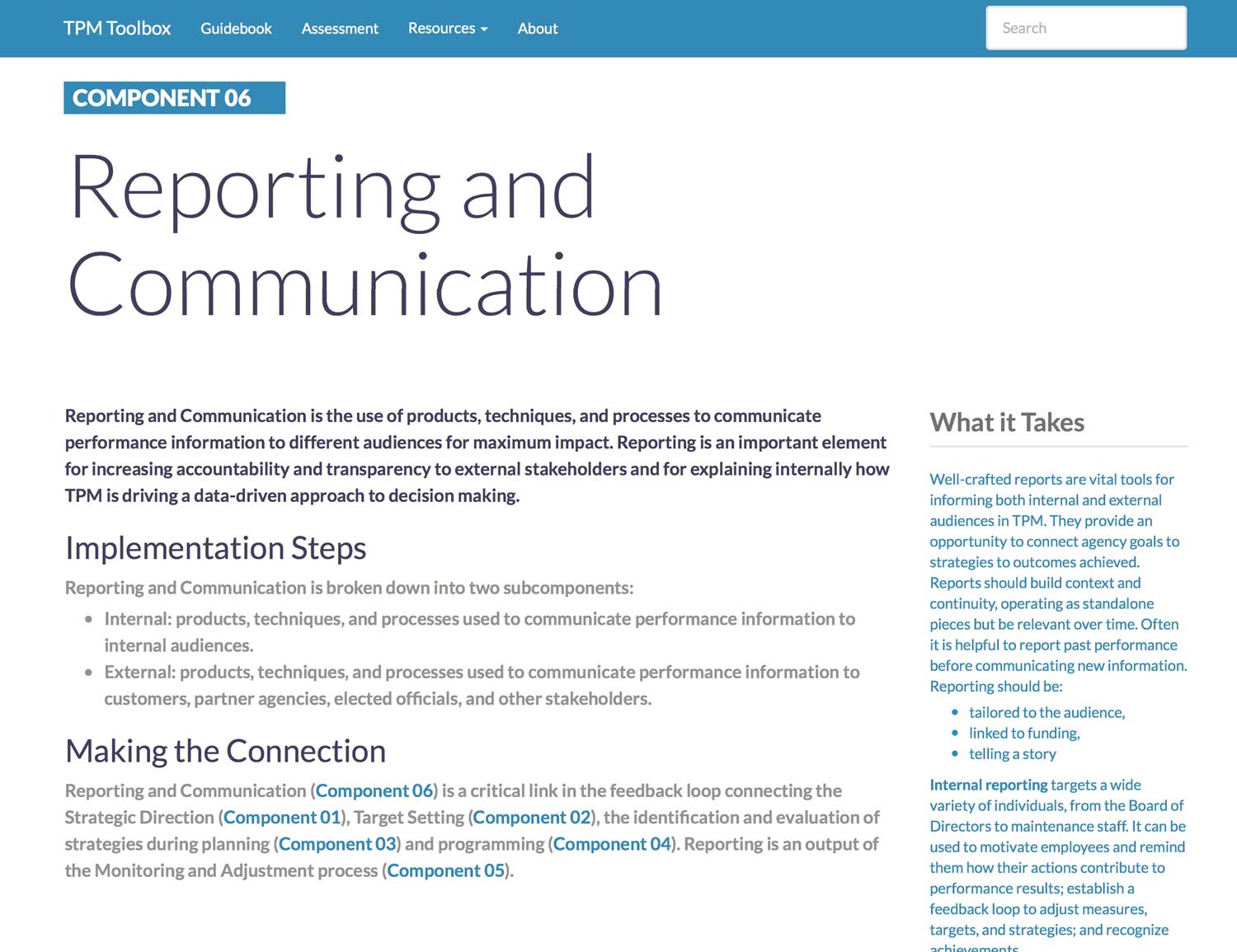
Component 6. Reporting and Communication
Reporting and Communication is the use of products, techniques, and processes to communicate performance information to different audiences for maximum impact. Reporting is an important element for increasing accountability and transparency to external stakeholders and for explaining internally how TPM is driving a data-driven approach to decision making.
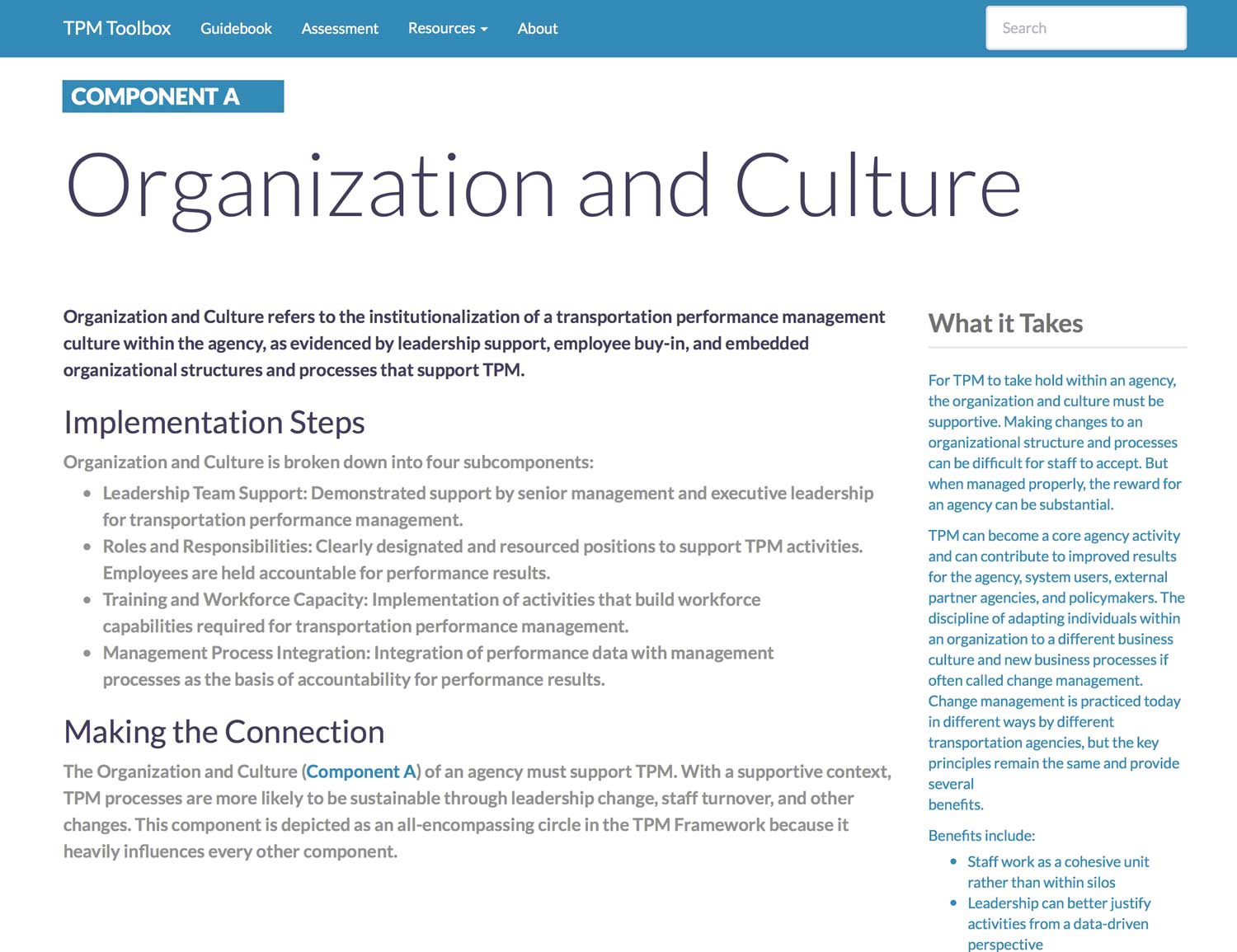
Component A. Organization and Culture
Organization and Culture refers to the institutionalization of a transportation performance management culture within the agency, as evidenced by leadership support, employee buy-in, and embedded organizational structures and processes that support TPM.
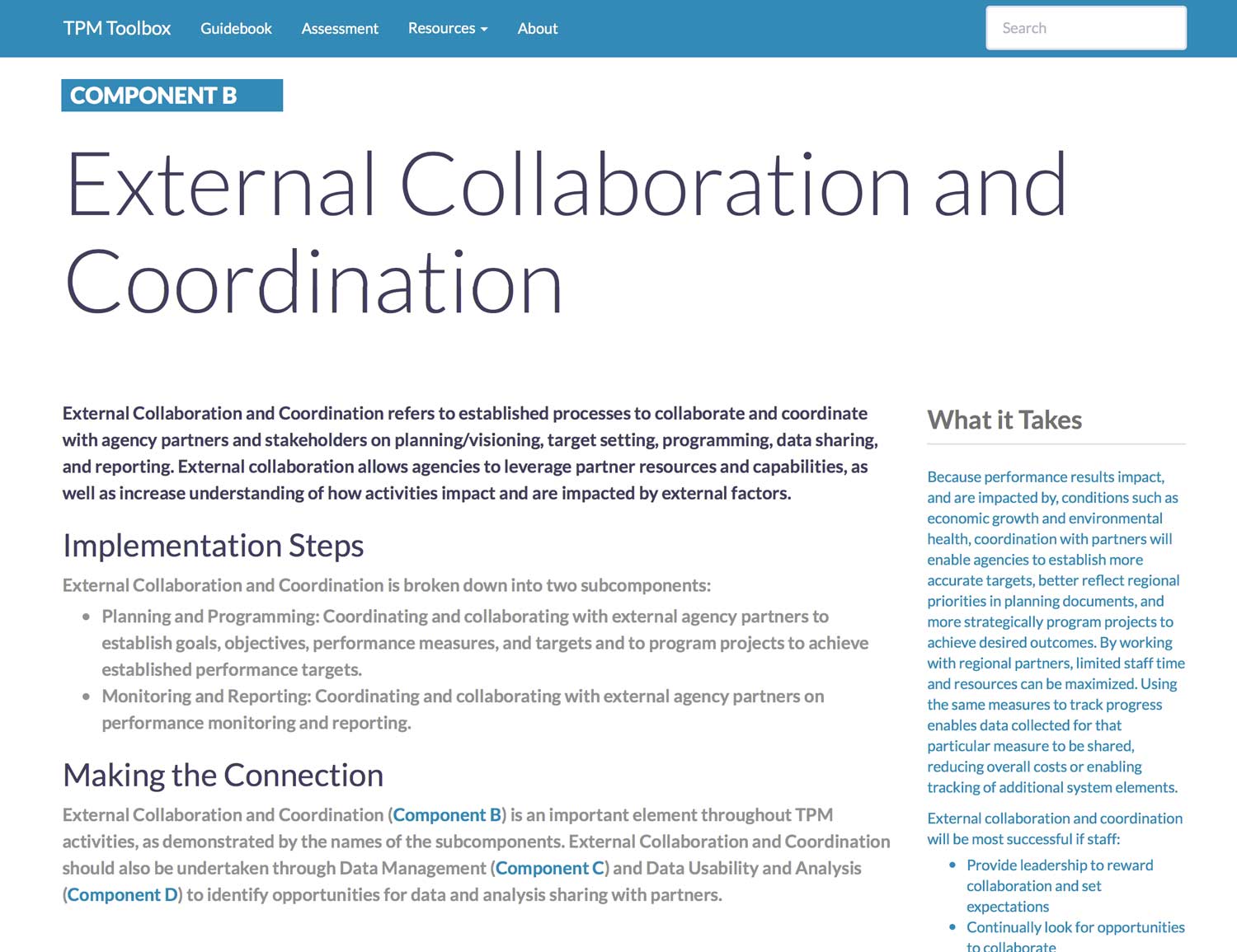
Component B. External Collaboration and Coordination
External Collaboration and Coordination refers to established processes to collaborate and coordinate with agency partners and stakeholders on planning/visioning, target setting, programming, data sharing, and reporting. External collaboration allows agencies to leverage partner resources and capabilities, as well as increase understanding of how activities impact and are impacted by external factors.
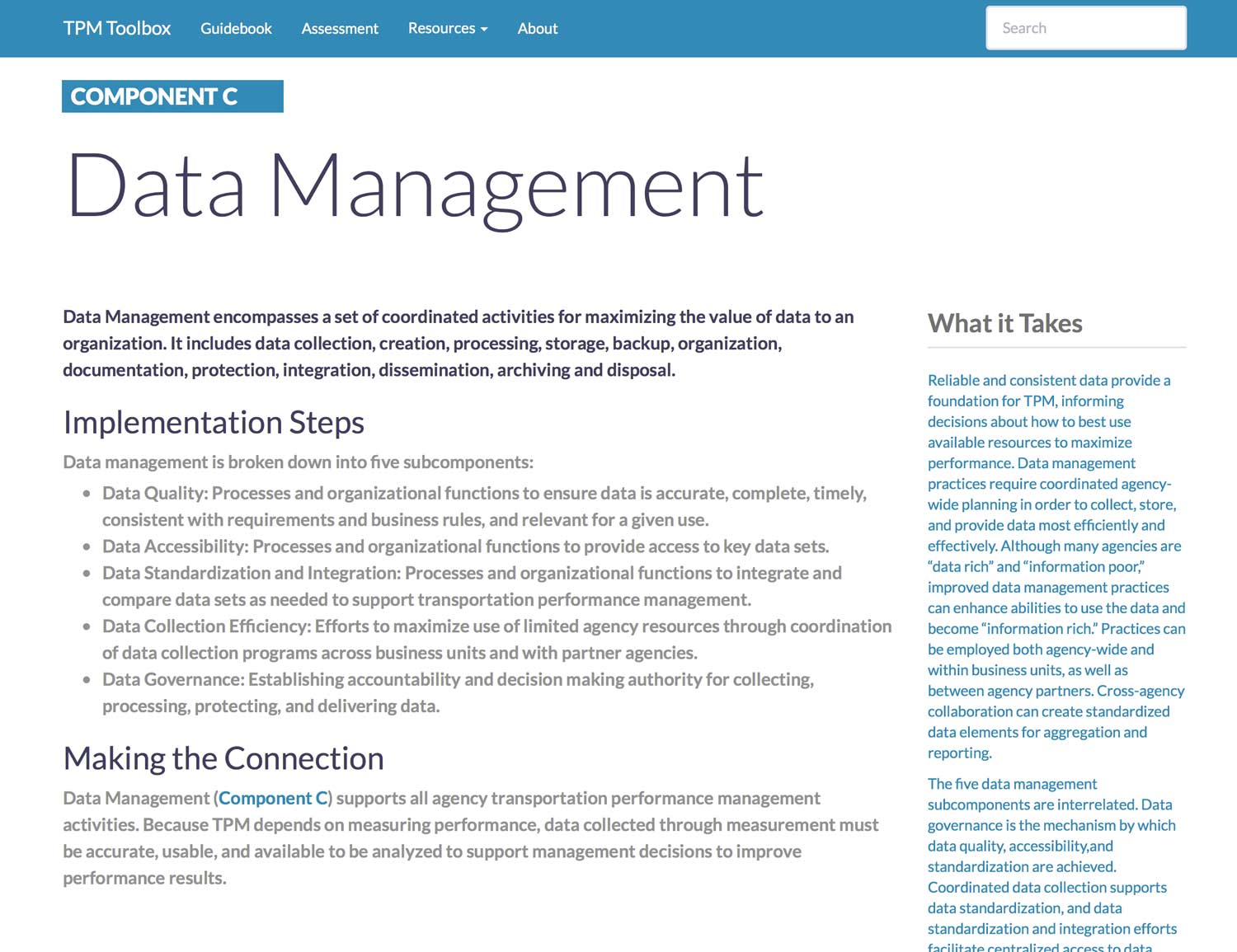
Component C. Data Management
Data Management encompasses a set of coordinated activities for maximizing the value of data to an organization. It includes data collection, creation, processing, storage, backup, organization, documentation, protection, integration, dissemination, archiving and disposal.
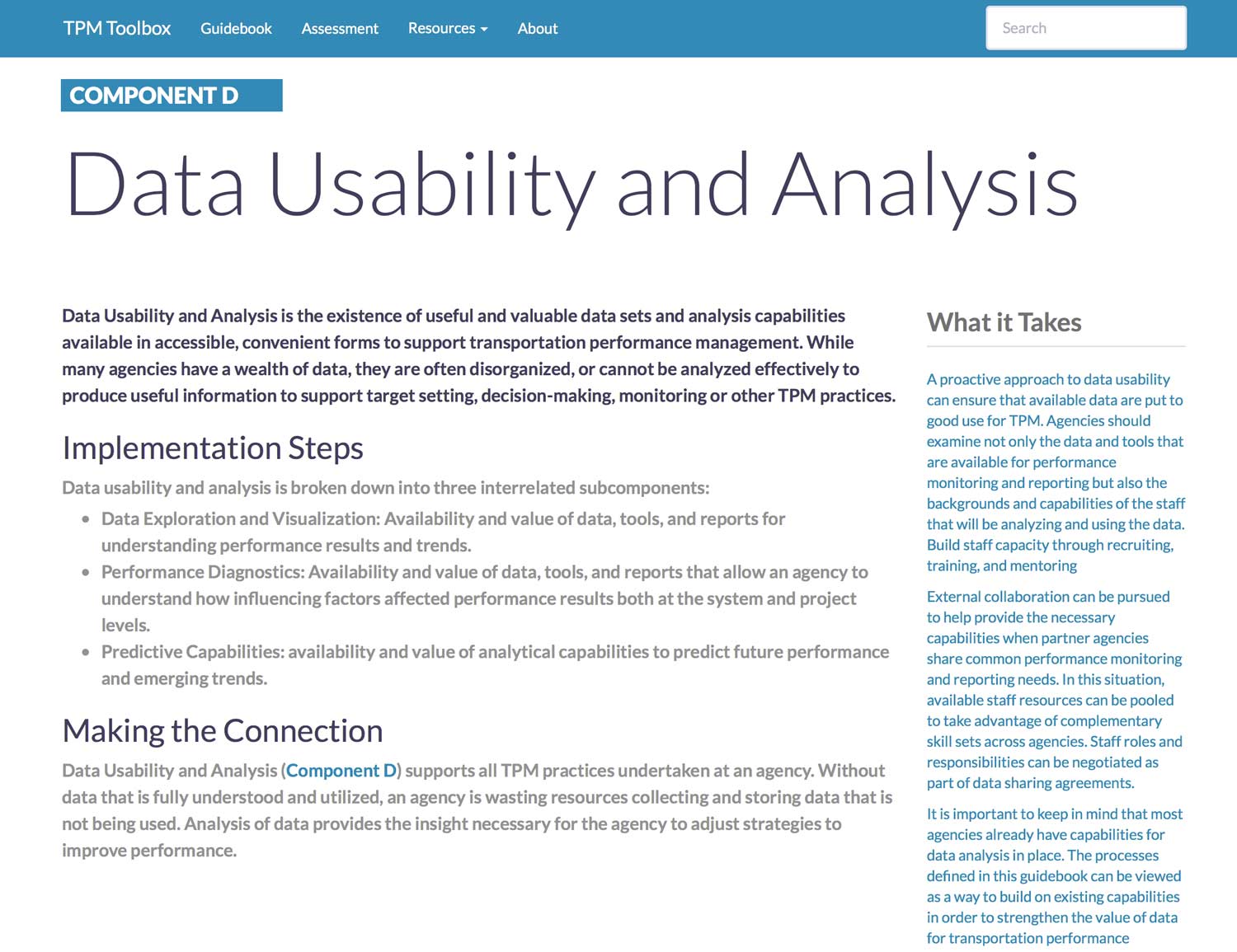
Component D. Data Usability and Analysis
Data Usability and Analysis is the existence of useful and valuable data sets and analysis capabilities available in accessible, convenient forms to support transportation performance management. While many agencies have a wealth of data, they are often disorganized, or cannot be analyzed effectively to produce useful information to support target setting, decision-making, monitoring or other TPM practices.